Technology that efficiently transfers energy from one place to another is a valuable commodity that scientists and organizations around the world are making great efforts to develop. Transferring energy, particularly energy that would otherwise be wasted, from one source and for repurposing in another application conserves resources, reduces costs and is beneficial to the environment. A heat pump is a high-tech device that essentially transfers heat from one place to another and this heat translates to energy that can be utilized in a number of thermal energy applications. Typically, heat pumps are used to draw heat from the air or ground in order to heat a building, but the process can also be reversed to cool a building through a process that is the core technology in an HVAC system.
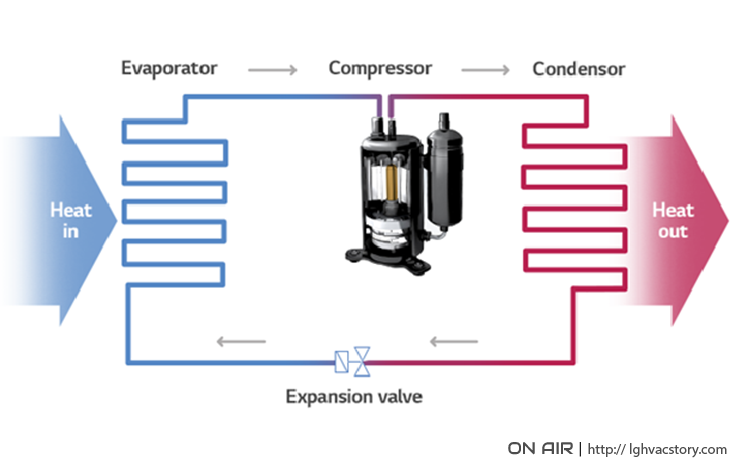
Basic Heat Pump Refrigerant Cycle
In the same way, a water pump works to transport water from one place to another, heat pumps are a solution that transfers heat energy. Like many air conditioning systems, heat pumps implement a fluid called refrigerant that is circulated through the system via a compressor. The refrigerant used in heat pumps is produced to possess specific physical properties throughout the different stages of the heat pump process. Following the flow of this refrigerant through a heat pump will help us understand how a heat pump works. As the refrigerant enters the compressor of the heat pump, it is a low-pressure, low-temperature gas, and when the refrigerant leaves the compressor, it is a high-pressure, high-temperature gas. The refrigerant then passes through a ‘hot-side’ heat exchanger and leaves as a condensed liquid.
As the refrigerant changes from gas to liquid in the heat exchanger, the heat from the refrigerant is transferred from the heat pump system into the air outside. It then passes through an expansion valve and is converted to a cool, lower-pressure combination of liquid and gas. This mixture then moves through a ‘cold-side’ heat exchanger and is converted entirely into a gas. The evaporation of the liquid into a gas causes the cold-side heat exchanger to absorb heat from the air inside the building and cools it. The refrigerant then goes back into the compressor and the cycle begins again.
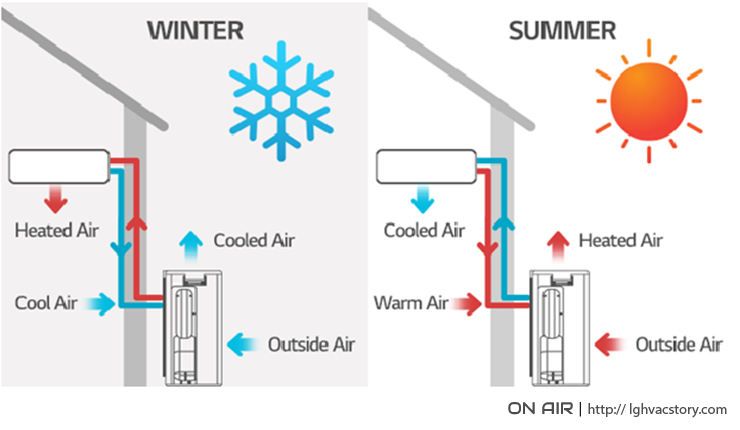
Heat pump cycles can be reversed
Heat pumps can, of course, be used as a heater by simply reversing the process cycle. The function of the heat pump stays the same with only the direction of heat transfer changing by use of a reversing valve. The refrigerant flow is reversed and the refrigeration cycle is changed from heating to cooling or cooling to heating. This means that the same building or facility can be heated and cooled by the same heat pump. The reversing valve can typically be controlled from a thermostat inside the building.
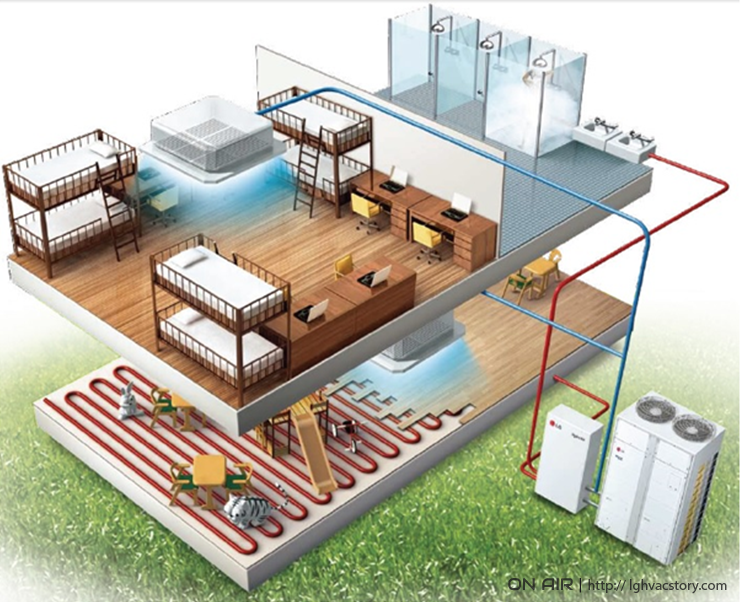
Heat pumps can supply heating and cooling to a home
The great thing about heat pumps is that it is possible to actually transfer more heat energy than the amount of energy required to operate the heat pumps themselves. This makes it appear as though heat pumps have an efficiency above 100%. While this is not really the case, as heat pumps only transfer energy, the best way to express the efficiency of a heat pump is through an index known as COP (Coefficient of Performance), which is represented by a ratio of Heat Energy Transported / Energy Input. You can find out more about COP and how it applies to energy efficiency and energy costs here: “SOLVING THE HVAC EFFICIENCY RATING PUZZLE – COP, EER, SEER”
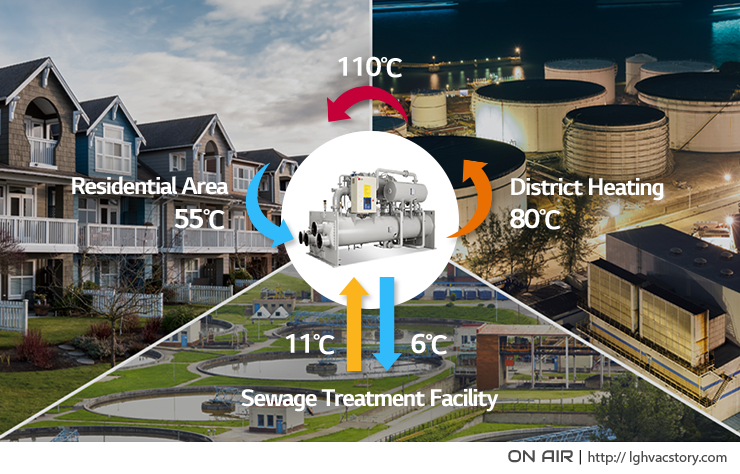
Heat pumps can provide usable heat energy from wasted heat
Heat pumps are also able to harness waste heat from sources such as wastewater from sewage treatment facilities, production plants, and power plants. Wastewater treatment plants produce large quantities of waste heat energy from sewage and other sources. This heat can be utilized by heat pumps to provide heat to other facilities in the immediate vicinity. Heat pumps using waste heat energy from wastewater are widely implemented in Europe, the US, Japan, South Korea and China. These heat pumps are efficient, reliable and economical sources of heat that utilize energy from various municipal facilities that would otherwise be wasted.
As we can see, heats pumps play an important role in keeping us comfortable year-round and, while we may not have been aware of how much we use them each day, we likely experience their effects quite often. This technology is allowing us to take advantage of previously wasted energy sources and they provide an efficient source of heating and cooling all in one device. LG develops their own heat pumps that function as the core driving technology in their world-class HVAC systems. There may be a heat pump closer to you right now than you think…it may even be one of LG’s very own.


































