Air conditioners and refrigerators are something many of us take advantage of on a daily basis. If we think about how much we use these devices and how complex these systems can be, they are truly amazing technologies. Various components and process go into making these systems work and one of the most integral parts that run these mechanisms is the compressor. The air conditioners in our homes and offices nearly all have mechanical compressors that are responsible for keeping us cool as the core component in air conditioning systems. In order to better understand how compressors work, let’s take a closer look at what they do to cool the air around us.
The air conditioners that most of us are familiar with have three major components that are key to keeping us cool. These components are the condenser, the evaporator, and the compressor. The role of the compressor is critical because it works as a mediator between the evaporator located inside of the building and the condenser located inside the building. Essentially, the compressor is responsible for converting the low-pressure, cool refrigerant from the evaporator into high-pressure, high-temperature gas refrigerant as it moves into the condenser.
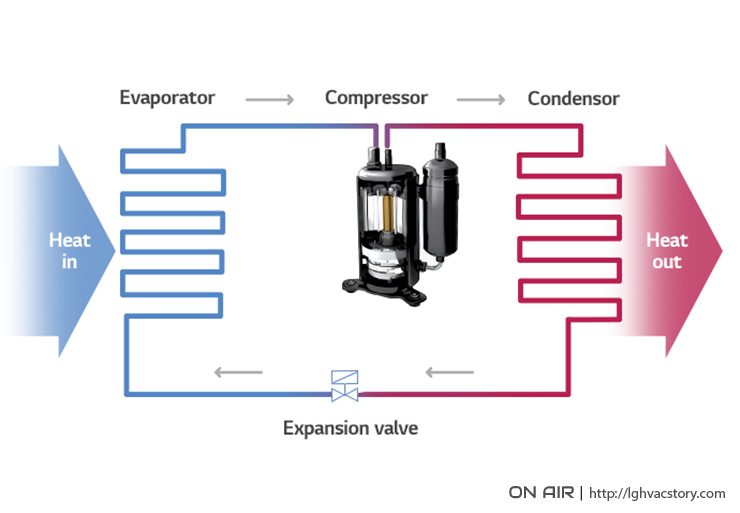
When low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant leaves the evaporator, it needs to be a higher temperature than the air outside of the building in order to release the heat accumulated inside the building. It’s at this point in the cooling process that the role of the compressor comes into play. Inside the compressor, the refrigerant is compressed into a high-pressure gas and the temperature rises. The refrigerant then flows into the condenser and heat from the refrigerant is transferred to the cooler outside air when the cooler air passes over the condenser coils. As the refrigerant temperature and pressure lowers, it converts back into a liquid and passed to the evaporator as the process is repeated.
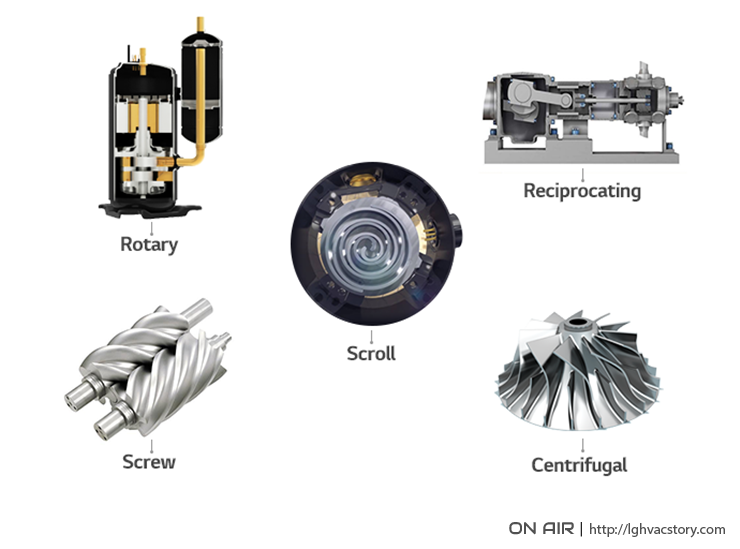
Depending on the type of system, a reciprocating, scroll, screw, rotary or centrifugal compressor can be implemented in an air conditioning system. Reciprocating compressors utilize a piston that moves in and out of a cylinder to create pressure and move refrigerant through the compressor. Scroll compressors have a stationary scroll and a rotating scroll that compress the refrigerant and discharge it through a port at the center of the scrolls. In screw compressors, a pair of rotors traps and compress refrigerant as they revolve within a cylinder. A rotary compressor has blades or vanes that rotate within a cylinder that compresses the refrigerant and forces it through an exhaust port. Finally, centrifugal compressors typically found in large capacity systems house a disc with radial blades that spin using centrifugal force and compress the refrigerant without valves, pistons or cylinders.
The LG Multi V 5 implements a scroll type compressor known as the Ultimate Inverter Compressor. The Ultimate Inverter Compressor is at the height of compressor efficiency, reliability and durability. Its widened operational range increases efficiency and allows the Multi V 5 to quickly reach desired temperatures. The advanced PEEK material used in the Multi V 5 bearing system allows the Multi V 5 to operate at extended periods of time without oil or maintenance. This next-generation technology is the core of the superior Multi V 5 air conditioning system.

While air conditioners are complex systems with many components, a well crafted compressor is at the heart of keeping these systems running efficiently and effectively. Most of us experience the effects of compressors on a daily basis in one way or another. So, this summer, when you feel the cool air from your air conditioner, give some thought to how that cool air is produced and how the compressor is working to make it possible. LG will continue to expand on the innovative compressor technology demonstrated in the Multi V 5 Ultimate Inverter Compressor and we will surely continue enjoying its effects.
The air conditioners that most of us are familiar with have three major components that are key to keeping us cool. These components are the condenser, the evaporator, and the compressor. The role of the compressor is critical because it works as a mediator between the evaporator located inside of the building and the condenser located inside the building. Essentially, the compressor is responsible for converting the low-pressure, cool refrigerant from the evaporator into high-pressure, high-temperature gas refrigerant as it moves into the condenser.

Air Conditioning Cooling Cycle
When low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant leaves the evaporator, it needs to be a higher temperature than the air outside of the building in order to release the heat accumulated inside the building. It’s at this point in the cooling process that the role of the compressor comes into play. Inside the compressor, the refrigerant is compressed into a high-pressure gas and the temperature rises. The refrigerant then flows into the condenser and heat from the refrigerant is transferred to the cooler outside air when the cooler air passes over the condenser coils. As the refrigerant temperature and pressure lowers, it converts back into a liquid and passed to the evaporator as the process is repeated.

Compressor Types
Depending on the type of system, a reciprocating, scroll, screw, rotary or centrifugal compressor can be implemented in an air conditioning system. Reciprocating compressors utilize a piston that moves in and out of a cylinder to create pressure and move refrigerant through the compressor. Scroll compressors have a stationary scroll and a rotating scroll that compress the refrigerant and discharge it through a port at the center of the scrolls. In screw compressors, a pair of rotors traps and compress refrigerant as they revolve within a cylinder. A rotary compressor has blades or vanes that rotate within a cylinder that compresses the refrigerant and forces it through an exhaust port. Finally, centrifugal compressors typically found in large capacity systems house a disc with radial blades that spin using centrifugal force and compress the refrigerant without valves, pistons or cylinders.
The LG Multi V 5 implements a scroll type compressor known as the Ultimate Inverter Compressor. The Ultimate Inverter Compressor is at the height of compressor efficiency, reliability and durability. Its widened operational range increases efficiency and allows the Multi V 5 to quickly reach desired temperatures. The advanced PEEK material used in the Multi V 5 bearing system allows the Multi V 5 to operate at extended periods of time without oil or maintenance. This next-generation technology is the core of the superior Multi V 5 air conditioning system.

LG Multi V 5 Ultimate Inverter Compressor
While air conditioners are complex systems with many components, a well crafted compressor is at the heart of keeping these systems running efficiently and effectively. Most of us experience the effects of compressors on a daily basis in one way or another. So, this summer, when you feel the cool air from your air conditioner, give some thought to how that cool air is produced and how the compressor is working to make it possible. LG will continue to expand on the innovative compressor technology demonstrated in the Multi V 5 Ultimate Inverter Compressor and we will surely continue enjoying its effects.
Related Post
INVISIBLE INNOVATIONS
INVISIBLE INNOVATIONS


































